How to set up Kubernetes Dashboard
1. Install Kubernetes Dashboard
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.3.1/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
You can check if the dashboard is installed by running the following command:
kubectl get ns
If you see kubernetes-dashboard namespace, it means the dashboard is installed.
You should be able to run the following command to see the dashboard pods and services:
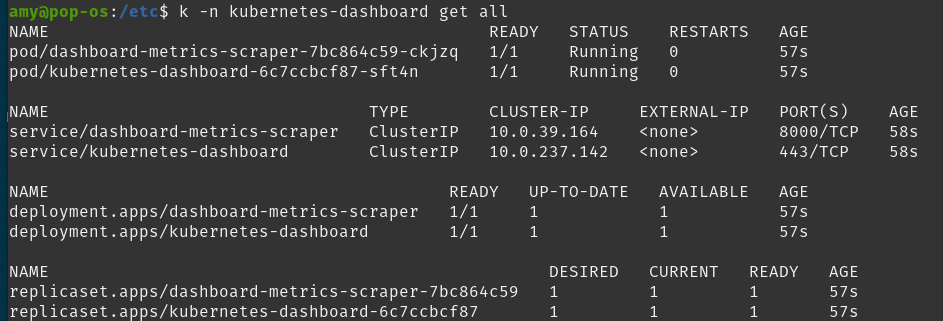
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get all
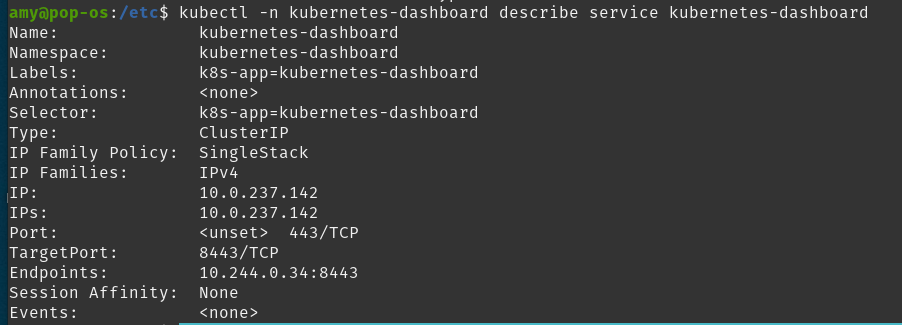
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard describe service kubernetes-dashboard
2. Access the dashboard
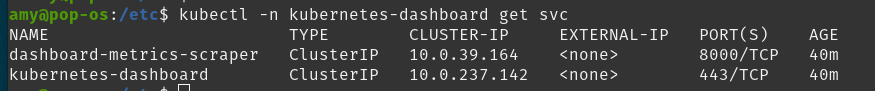
When you run the following command, you should see the dashboard service does not have an external IP address.
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get svc
2.1. Access the dashboard using port-forwarding
When you described the dashboard service, you should see the target port is 8443. You can use port-forwarding to access the dashboard. Make sure to use the correct pod name shown in the kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get all command.
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard port-forward kubernetes-dashboard-6c7ccbcf87-sft4n 8000:8443
Now you should be able to access the dashboard at https://localhost:8000/
2.2. Access the dashboard using a proxy
When you need to access the dashboard only when you needed, you can use a proxy. Using proxy will expose the dashboard outside the cluster while the proxy is running.
You can use the following command to start a proxy:
kubectl proxy
2.3. Access the dashboard using a NodePort
You can also use a NodePort to access the dashboard. You can use the following command to create a NodePort service:
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard edit svc kubernetes-dashboard
Then find type: ClusterIP and change it to type: NodePort. You can run the following command to see the dashboard service has NodePort type now. You can also add a port number to the nodePort field. If you don’t specify the port number, Kubernetes will assign a random port number. Here, I used 32323 as the port number, which I added under the targetPort field.
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get svc
Now, get the internal IP address of the node by running the following command:
kubectl get nodes -o wide
Finally, you can add the IP address to your hosts file. For linux, you can find the hosts file at /etc/hosts. For Windows, you can find it at C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts. Add the following line to the hosts file:
cat /etc/hosts
Copy the IP address of the node and add it to the hosts file. Then Ctrl + D to save and exit.
Now, you should be able to access the dashboard at https://<node-name>:32323/.
2.4. Access the dashboard using an Ingress
This is the method that I will be using. First, check your DNS provider and make sure you have a domain name. I’m going to use subdomain for my dashboard.
Then, you need to install an Ingress controller. I’m using Nginx Ingress controller. You can install it by running the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.8.1/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml
You can check if the Ingress controller is installed by running the following command:
kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx
Now, create a namespace for the dashboard:
kubectl create ns kubernetes-dashboard
Then, create an ingress.yaml file:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: dashboard-ingress
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard #should match with service and pod
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTPS"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: dashboard.amyapproved.me
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: kubernetes-dashboard
port:
number: 443
Kubernetes dashboard uses HTTPS by default. So, you need to add nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTPS" to the annotations. Also, make sure to add the correct host name. You can use kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard to get the service name and port number.
I had some trouble with the ingress. So I ran kubectl -n <namespace> port-forwad <servicename> <portnumber> to make sure the service is working. Then I ran kubectl -n <namespace> describe svc <servicename> to see if the service is using the correct port number. I also ran kubectl -n <namespace> describe ingress <ingressname> to see if the ingress is using the correct service name and port number.
In my case, it looked like this:
kubectl -n ingress-nginx port-forward service/ingress-nginx-controller 8000:80
Then I went to http://localhost:8000/ and confirmed that the service is working locally.
Below command gave me the IP address of the ingress controller which I pointed my domain A name to. Then I pointed CNAME to that A name.
k describe svc ingress-nginx-controller -n ingress-nginx
I burned my long weekend setting up this kubernetes dashboard. I hope this post will save you some time!